NanoSync Engine Guide #
Introduction #
NanoSync engine(trigger handler block) which can be used to perform many real-time events or tasks without the CPU’s intervention.
The NanoSync engine operates based on triggers and handlers. When a trigger (also called an event) happens, a handler will be invoked. A handler consists of a sequence of hardware actions (also called hardware tasks), which can be automatically executed by the hardware without the CPU intervention. Typical triggers include GPIO input status change, timer time out, CPU interrupts etc.
Terminology #
Priority Queues #
NanoSync engine supports three priority queues:
High Priority Queue:
- Supports up to 8 defined triggers.
- Dedicated memory of 512 words.
Middle Priority Queue:
- Supports up to 8 defined triggers.
- Use shared memory, maximum memory usage is 512 words.
Low Priority Queue:
- Supports up to 16 defined triggers.
- Use shared memory, maximum memory usage is 512 words.
Higher priority queue can preempt lower priority queue.
Trigger id #
In each queue, there are multiple triggers. And each trigger is assined a unique trigger id. The high priority and middle priority queues have 8 triggers, with trigger id ranging from 0 to 7. The low priority queue has 16 triggers, with trigger id ranging from 0 to 15.
When multiple triggers within the same queue are triggered simultaneously, the trigger with the smallest trigger id will be executed first.
Trigger Header #
Every trigger has a header. Trigger headers are located at beginning of queue memory.
Trigger Signals #
There are 255 trigger signals. And 0xFF is invalid trigger signal(refer to enum trig_cond_idx for details). Each trigger signal corresponds to an external or internal signal. When receive the signal(rising edge/failling edge), it triggers the corresponding trigger and executing the corresponding trigger command.
Trigger Command #
A trigger can have multiple trigger commands. When activated, these commands will be executed sequentially.
ODC(output direct controls) #
Used by output command. Has 127 output direct controls(refer to enum trig_odc_idx for details).
Memory #
High priority queue has 512 words(2KB) dedicated memory(trig memory). Middle and low priority queue use shared memory.
Timer #
Each priority queue has its own 24-bit timer.
AHB/APB bus #
Trigger handler can use APB or AHB bus to access peripheral registers.
AHB bus: CPU can access register with AHB bus. Read and write opertations don’t have a fix lantency. The deviation is about 3us.
APB bus: CPU can’t access register with APB bus. Has fix latency, The deviation is less than 0.1us.
Trigger Address #
All trigger API use word address offset, not byte address. Address offset is start from 0x0.
Trigger configuration #
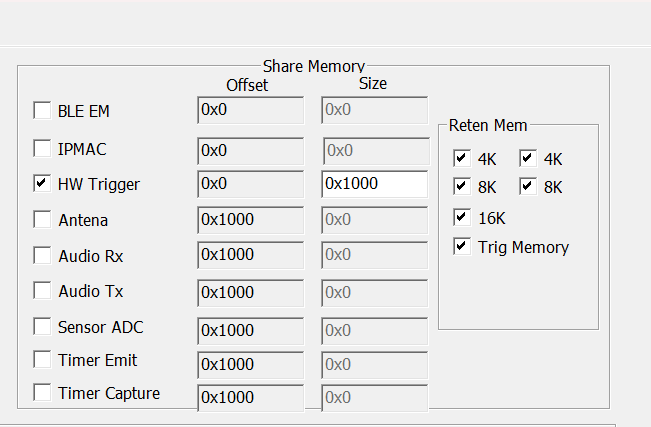
Enable HW trigger in share memory configuration. The size is low priority queue memory size plus middle priority queue memory size. Maximum size is 4K(0x1000). If enable sleep, should select “Reten Mem” to retention shared memory and trigger memory.
Trigger command #
Set timer command #
This commamnd is used to config the timer.The timer will be initialized with the initial value specified by the command (or the value in the control register) and will start counting down towards 0. If the auto-reload bit of the command is set to 0x1, the timer will restart with the initial value or the value from the control register after reaching 0. If the auto-reload bit of the command is set to 0x0, the timer will stop. If the timer is already running at the time of this command execution, it will be reset to the initial value and restart. Upon reaching 0, the timer can generate an interrupt signal.
Wait timer command #
This command is used to wait for the timer to expire. This command will block the subsequent commands until the timer reaches the value specified in the command. If the “stop timer” bit is 1, the timer will stop counting when the timer reaches the expected value. If the “stop timer” bit is 0, the timer will continue counting after it reaches the expected value. It is strongly recommended that this command is NOT used in the highest priority queue as this command might delay the execution of all following triggers in the highest priority queue and also all triggers in the middle and lowest priority queues.
Register read and compare command #
This command reads a value from a specific register, applies the mask on the read value and then compares the masked value to the expected value. When conditions fails, it can jump to another address to run command.
Register write command #
This command write 32 bits value to register.
Register read and write command #
The command reads the register value first and only update the bits to the write value where the corresponding bits in the mask is 1. The actual write value is computed as:
actual_write_value = (read_value & ( ~ mask )) | (write_value & mask).
Register copy command #
This command will read the source register address value, and copy data to destination register.
Register copy with mask command. #
This command will read the source register address value, apply the mask and write the masked value to the destination register address. The destination register value will also be read and the non-mask portion will be unchanged and written back to the destination register address together with the masked source register read value.
written_value = (destination_read_value & (~ mask)) | (source_read_value & mask).
Output command #
This command output signal with ODC(output direct controls). Refer to enum trig_hdl_idx for specific signal details. Each output command contains an output signal index, a toggle enable and an output value. If the index is larger than 127, the specific ODC is disabled. It is recommended to write 0x7F to all unused output signal index. If the toggle bit is 1 for a given output index, the corresponding output value will be ignored and the corresponding output signal will toggle its current output value to an opposite polarity.
Notice that we will use a control register to initialize the output port value which will be controlled by the trigger handler before the handler module is enabled. See hal_trig_hdl_gpio_out_en for reference.
Null command #
This command is just a placeholder in the memory and will not execute any operation.