Inplay SMULL Command Set For Transparent Data Transmission #
Introduction #
IN618 is InPlay’s SMULL SoC product which features synchronous multi-node low-latency protocol (SMULL) stack with 2.4Ghz frequency band RF radio and MCU system integrated. The device incorporates an InPlay SMULL radio and subsystem that contains the RF transceiver, baseband, PHY and link layer engines.The physical layer has the digital PHY and RF transceiver that transmits and receives GFSK packets at 2Mbps. The PHY can also be configured to 1Mbps mode to transmits and receives 1Mbps modulated packets.
The baseband controller combines both hardware and software implementation that supports variety of communication modes between master and slave devices: Unicast, multi-cast and broadcast modes. In a typical start topology network, as shown in Figure 1, the central node will operate as the master and the peripheral nodes will operate as the slave nodes. The communication between the master and the slaves can be unidirectional or bi-directional.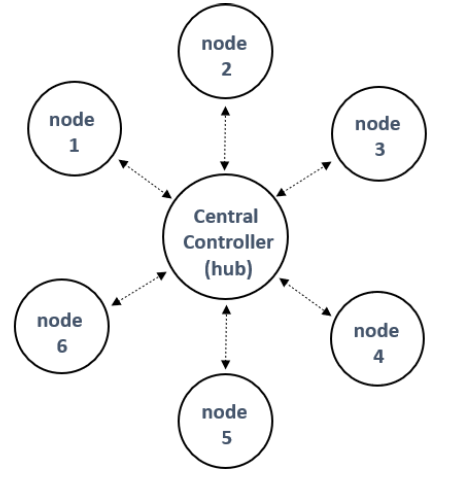
The baseband controller can be configured as either master or slave operation mode. The communication between the master and the slaves is framed based communication as shown in Figure 2. On each frame, the master sends a broadcast packet, or a public packet, or a downlink private packet (DPP) to each of the slaves. As illustrated in Figure 2, assume there are N slaves,and each slave has a unique ID number from {0, 1, 2, …, N-1}. Each salve can send an uplink private (UP) packet at the assigned time (t0, t1, …,) in the frame to the master. The packets sent from the master share the same preamble and sync address. Each packet from the slave has its own preamble and sync address. And all the timing critical functions in the baseband controller are implemented in hardware such as CRC, data whitening and access address detection.
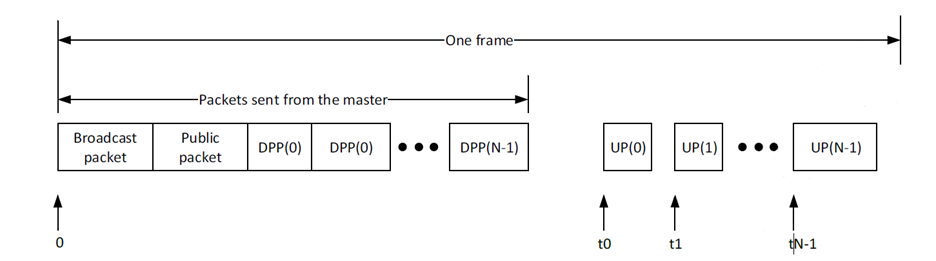
The data exchange can be configured to operate in three different modes between a master and multiple salves.
Private data exchange mode
The master can be configured to send each slave a private packet at each frame. Each slave can be configured to send the master a private packet at each frame.
Private packet: There is acknowledgement between the sender and the recipient.
Public data exchange mode
The master can be configured to send a public packet to all the slaves at each frame.
Public packet: Slaves do the acknowledgement. The master does not proceed to next public packet unless the current public packet is acknowledged by all the slaves.
Broadcasting mode
The master can be configured to send a broadcast packet to all the slaves at each frame.
Broadcast packet: Slaves do not acknowledge the reception of a broadcast packet.
Overview of transparent data transmission #
Many modern applications rely on wireless data transmission; however, end-users often lack knowledge or interest in the underlying wireless technologies. Consequently, we have designed a mechanism that allows users to conveniently utilize the powerful data transfer capabilities provided by SMULL without the need to understand the details of this protocol. Before starting the data transmission, it is necessary to configure the relevant parameters of SMULL to establish a network between the master and slave. By using the commands we provide, you can quickly establish the SMULL network. Please refer to the example provided below for more details. The schematic of the entire system, showing the connection between the host and IN618 module, is illustrated in Figure 3.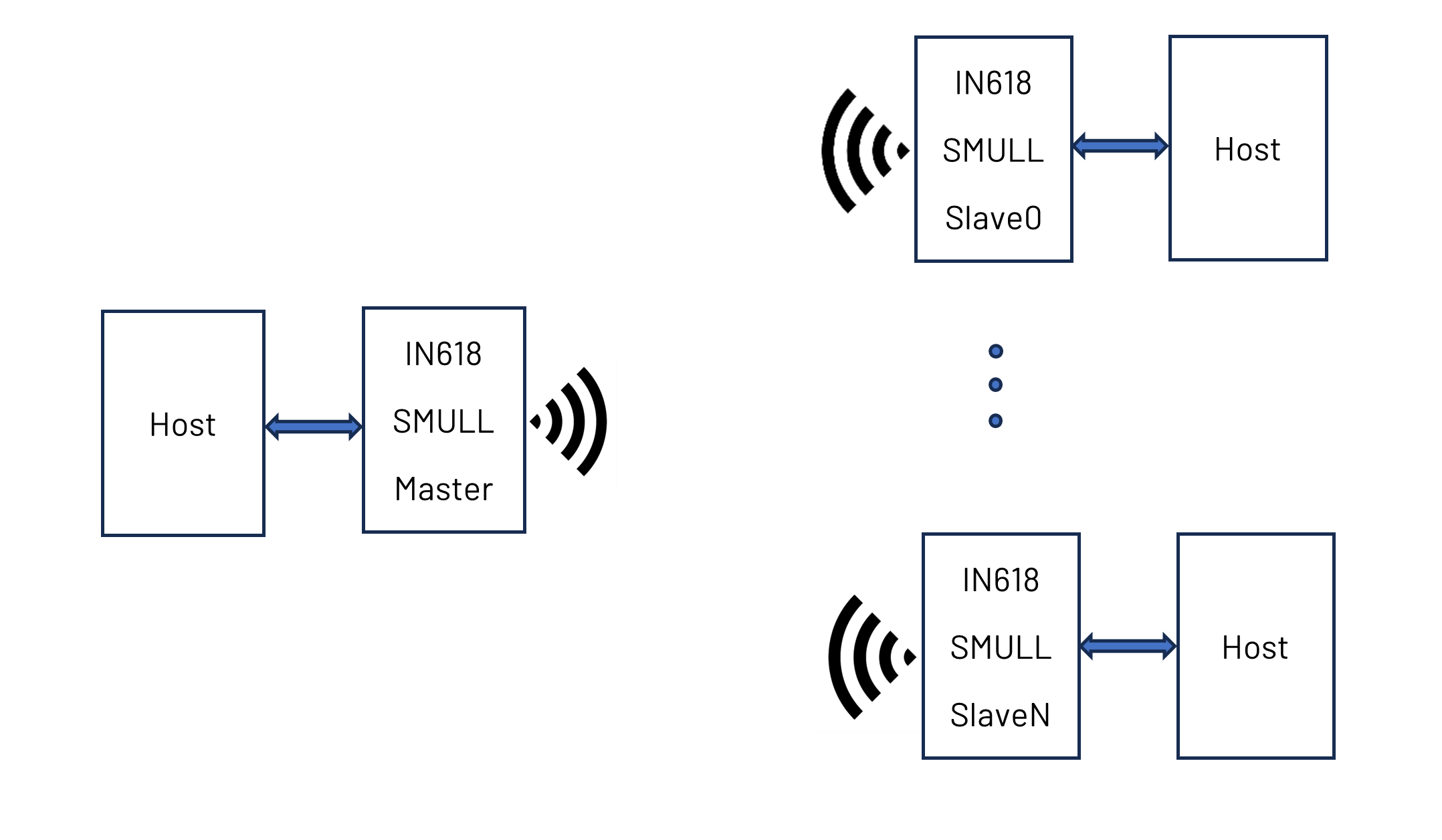 Typically, the host refers to various devices such as personal computers (PCs), laptops, microcontroller units (MCUs), and others. In the current architecture, the host and IN618 communicate through UART. The default settings for the UART in our system are illustrated below.
Typically, the host refers to various devices such as personal computers (PCs), laptops, microcontroller units (MCUs), and others. In the current architecture, the host and IN618 communicate through UART. The default settings for the UART in our system are illustrated below.
UART default settings #
- 115,200 bps
- 8 bits
- No Parity
- 1 Stop bit
- Hardware flow control disabled
The uart configuration command can be used to modify the UART settings.
Command Set #
In order to facilitate software development with SMULL, we have designed a set of commands for programming. Users can effortlessly start the system by utilizing these commands.The command format is shown as following.
| Command Code | Data Length | Data |
|---|---|---|
| 2 bytes | 2 bytes | variable bytes |
Get Slave Number: 0xA011 #
This command gets the number of slaves in current network.
Send: 0xA0 0x11 0x00 0x00
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x11 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (LSB) |
Response: 0xA0 0x11 0x00 0x01 B0
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x11 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x01 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | Number of slaves |
Set Slave Number: 0xA012 #
This command is used to configure the number of slaves.The slave number should be less than (or equal to) the maximum slave number (CFG_IPMAC_MAX_SLV_NUM).
Send: 0xA0 0x12 0x00 0x01 B0
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x12 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x01 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | Number of slaves |
Response: 0xA0 0x12 0x00 0x01 B0
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x12 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x01 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | B0=0x00: success B0=0x01: the command sent is too short B0=0x02: number of slave is larger than the maximum value |
Notice:
After successfully setting the slave number on the master side, the corresponding next steps should be taken based on whether the network has already been established.
① If the network has been established, you may want to broadcast the new settings to all slaves. Thus, you should issue the command 0xA040 to request the master broadcast new settings. After the completion of the broadcast, you will receive a response. Once you have successfully received the response, it is necessary to reset the chip by issuing the command 0xA0E1.
② If the network has not yet been established, broadcasting the new settings is unnecessary. So, you can reset the chip by issuing the command 0xA0E1.
After successfully setting the slave number on the slave side, the chip needs to be reset immediately by issuing the command 0xA0E1.
Get Slave ID: 0xA013 #
This command gets the slave ID.
Send: 0xA0 0x13 0x00 0x00
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x13 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (LSB) |
Response: 0xA0 0x13 0x00 0x01 B0
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x13 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x01 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | Slave ID |
Set Slave ID: 0xA014 #
This command sets the slave ID on the slave side. Sending this command to the master will not receive any response. Each slave in a network must have a unique ID.
Send: 0xA0 0x14 0x00 0x01 B0
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x14 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x01 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | Slave ID |
Response: 0xA0 0x14 0x00 0x01 B0
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x14 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x01 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | B0=0x00: success B0=0x01: The command sent is too short B0=0x02: Slave ID is larger than or equal to the slave number which you set. |
Notice:
After successful configuration, you must reset the chip by issuing the command 0xA0E1, otherwise, the slave ID will not be updated.
Get SYNC Address (Network Address): 0xA015 #
This command gets the SYNC address. Each established network should have a unique SYNC address (also known as network address).
Send: 0xA0 0x15 0x00 0x00
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x15 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (LSB) |
Response: 0xA0 0x15 0x04 B0 B1 B2 B3
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x15 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x04 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | SYNC Address (MSB) |
| B1 | SYNC Address |
| B2 | SYNC Address |
| B3 | SYNC Address (LSB) |
SYNC Address = (B0 « 24) | (B1 « 16) | (B2 « 8) | B3
Set SYNC Address (Network Address): 0xA016 #
This command can be used to set the SYNC address. The value 0x00000000 will be ignored and the address will not be updated. The value 0xFFFFFFFF also cannot be accepted.
Send: 0xA0 0x16 0x00 0x04 B0 B1 B2 B3
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x16 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x04 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | SYNC Address (MSB) |
| B1 | SYNC Address |
| B2 | SYNC Address |
| B3 | SYNC Address (LSB) |
Response: 0xA0 0x16 0x00 0x01 B0
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x16 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x01 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | B0=0x00: success B0=0x01: The command sent is too short B0=0x02: SYNC address is invalid. |
Notice:
For optimal performance, it is advisable to ensure that the SYNC address bit sequence does not contain four consecutive ones or zeros. Generally speaking, it is better to use a random value. For example,
0x2954935B is a good value. There are no 4 consecutive ones or zeros in its bit sequence.
0x10F10724 is not a good value. There are 4 consecutive ones or zeros in its bit sequence.
After successfully setting the SYNC address on the master side, the corresponding next steps should be taken based on whether the network has already been established.
① If the network has been established, you may want to broadcast the new settings to all slaves. Thus, you should issue the command 0xA040 to request the master broadcast new settings. After the completion of the broadcast, you will receive a response. Once you have successfully received the response, it is necessary to reset the chip by issuing the command 0xA0E1.
② If the network has not yet been established, broadcasting the new settings is unnecessary. So, you can reset the chip by issuing the command 0xA0E1.
After successfully setting the SYNC address on the slave side, the chip needs to be reset immediately by issuing the command 0xA0E1.
Get PHY Rate: 0xA017 #
This command gets the PHY rate. The supported PHY rates are 1Mbps and 2Mbps.
Send: 0xA0 0x17 0x00 0x00
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x15 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (LSB) |
Response: 0xA0 0x17 0x00 0x01 B0
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x17 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x01 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | B0=0x01: 1Mbps B0=0x02: 2Mbps |
Set PHY Rate: 0xA018 #
This command can be used to set the PHY rate.
Send: 0xA0 0x18 0x00 0x01 B0
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x18 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x01 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | B0=0x01: 1Mbps B0=0x02: 2Mbps |
Response: 0xA0 0x18 0x00 0x01 B0
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x18 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x01 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | B0=0x00: success B0=0x01: The command sent is too short B0=0x02: PHY Rate is invalid. |
Notice:
After successfully setting the PHY rate on the master side, the corresponding next steps should be taken based on whether the network has already been established.
① If the network has been established, you may want to broadcast the new settings to all slaves. Thus, you should issue the command 0xA040 to request the master broadcast new settings. After the completion of the broadcast, you will receive a response. Once you have successfully received the response, it is necessary to reset the chip by issuing the command 0xA0E1.
② If the network has not yet been established, broadcasting the new settings is unnecessary. So, you can reset the chip by issuing the command 0xA0E1.
After successfully setting the PHY rate on the slave side, the chip needs to be reset immediately by issuing the command 0xA0E1.
Get Mode: 0xA019 #
This command gets the current mode.
Send: 0xA0 0x19 0x00 0x00
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x19 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (LSB) |
Response: 0xA0 0x19 0x00 0x01 B0
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x17 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x01 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | B0=0x00: slave B0=0x01: master |
Set Mode: 0xA01A #
This command is used to set the mode (master or slave) on the device. Each device will be configured as a master or a slave. In a network, only one device can be configured as a master.
Send: 0xA0 0x1A 0x00 0x01 B0
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x1A | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| B0 | B0 should be 0 (slave) or 1 (master), other values are considered as invalid. |
Response: 0xA0 0x1A 0x00 0x01 B0
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x1A | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x01 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | B0=0x00: success B0=0x01: The command sent is too short B0=0x02: Mode is invalid. |
Notice:
After successful configuration, you must reset the chip by issuing the command 0xA0E1, otherwise, the mode will not be updated.
Get Maximum Length of Downlink Private Packet: 0xA01B #
This command gets the maximum length of downlink private packet. Here, the downlink means the data are transmitted from master to slave.
Send: 0xA0 0x1B 0x00 0x00
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x1B | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (LSB) |
Response: 0xA0 0x1B 0x00 0x02 B0 B1
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x1B | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x02 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | maximum length of downlink private packet (MSB) |
| B1 | maximum length of downlink private packet (LSB) |
Length = (B0 « 8) | B1
Set Maximum Length of Downlink Private Packet: 0xA01C #
The default length of downlink private packet is 6 bytes. Ensure that the value you set is equal to or greater than 6. This length should be less than 200.
Send: 0xA0 0x1C 0x00 0x02 B0 B1
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x1C | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x02 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | maximum length of downlink private packet (MSB) |
| B1 | maximum length of downlink private packet (LSB) |
Response: 0xA0 0x1C 0x00 0x01 B0
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x1C | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x01 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | B0=0x00, success; B0=0x01, The command sent is too short; B0=0x02, Length is larger than the limitation (200 bytes). |
Notice:
After successfully setting the maximum length of downlink private packet on the master side, the corresponding next steps should be taken based on whether the network has already been established.
①If the network has been established, you may want to broadcast the new settings to all slaves.Thus, you should issue the command 0xA040 to request the master broadcast new settings. After the completion of the broadcast, you will receive a response. Once you have successfully received the response, it is necessary to reset the chip by issuing the command 0xA0E1.
②If the network has not yet been established, broadcasting the new settings is unnecessary. So, you can reset the chip by issuing the command 0xA0E1.
After successfully setting the maximum length of downlink private packet on the slave side, the chip needs to be reset immediately by issuing the command 0xA0E1.
Get Maximum Length of Uplink Private Packet: 0xA01D #
the maximum length of uplink private packet. Here, the uplink means the data are transmitted from slave to master.
Send: 0xA0 0x1D 0x00 0x00
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x1D | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (LSB) |
Response: 0xA0 0x1D 0x00 0x02 B0 B1
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x1D | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x02 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | Maximum length of uplink private packet (MSB) |
| B1 | Maximum length of uplink private packet (LSB) |
Set Maximum Length of Uplink Private Packet: 0xA01E #
This length should be less than 200.
Send: 0xA0 0x1E 0x00 0x02 B0 B1
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x1E | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x02 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | Maximum length of uplink private packet (MSB) |
| B1 | Maximum length of uplink private packet (LSB) |
Response: 0xA0 0x1E 0x00 0x01 B0
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x1E | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x01 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | B0=0x00: success B0=0x01: The command sent is too short B0=0x02: Length is larger than the limitation (200 bytes). |
Notice:
After successfully setting the maximum length of uplink private packet on the master side, the corresponding next steps should be taken based on whether the network has already been established.
①If the network has been established, you may want to broadcast the new settings to all slaves.Thus, you should issue the command 0xA040 to request the master broadcast new settings. After the completion of the broadcast, you will receive a response. Once you have successfully received the response, it is necessary to reset the chip by issuing the command 0xA0E1.
②If the network has not yet been established, broadcasting the new settings is unnecessary. So, you can reset the chip by issuing the command 0xA0E1.
After successfully setting the maximum length of uplink private packet on the slave side, the chip needs to be reset immediately by issuing the command 0xA0E1.
Get Period of Heartbeat Packet: 0xA033 #
In order to track the connection status of the network, heartbeat packet is periodically sent between the master and slave(s). Users can get the period of the heartbeat packet by issuing this command. The default value is 1000ms.
Send: 0xA0 0x33 0x00 0x00
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x33 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (LSB) |
Response: 0xA0 0x33 0x00 0x04 B0 B1 B2 B3
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x33 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x04 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | Period (MSB) |
| B1 | Period |
| B2 | Period |
| B3 | Period (LSB) |
Set Period of Heartbeat Packet: 0xA034 #
Users can change the period of the heartbeat packet by issuing this command.
Send: 0xA0 0x34 0x00 0x04 B0 B1 B2 B3
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x34 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x04 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | Period (MSB) |
| B1 | Period |
| B2 | Period |
| B3 | Period (LSB) |
If the period is zero, the default value (1000ms) will be used.
Response: 0xA0 0x34 0x00 0x01 B0
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x34 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x01 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | B0=0x00:success B0=0x01:The command is too short |
Notice:
The minimum heartbeat period is 500ms. Thus, the period you set should be larger than or equal to 500ms. If the period is less than 500ms, it will be automatically set to 500ms.
Broadcast SMULL Settings: 0xA040 #
With this command, the master can broadcast the SMULL settings. Once the network has been established, the master can use this command to broadcast the new SMULL-related parameters to all the slaves. The slave will update its settings and reset automatically upon receiving new settings broadcasted by the master.
Send: 0xA0 0x40 0x00 0x04 B0 B1 B2 B3
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x40 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x04 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | Broadcast Duration (MSB) |
| B1 | Broadcast Duration |
| B2 | Broadcast Duration |
| B3 | Broadcast Duration (LSB) |
The broadcast duration in milliseconds indicates how long the broadcast will last. If this value is set to zero, the default value of 3000ms is utilized. To ensure successful reception by each slave, it is recommended to set this value to a minimum of 3000ms.
Response: 0xA0 0x40 0x00 0x01 B0
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x40 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x01 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | B0=0x00: Success B0=0x01: The command is too short B0=0x02: In slave mode, this command will be ignored |
Get SMULL status: 0xA041 #
This command gets the current status of SMULL.
Send: 0xA0 0x41 0x00 0x00
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x41 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (LSB) |
Response: 0xA0 0x41 0x00 0x01 B0
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x41 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x01 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | B0=0x00: It means the SMULL is successfully initialized B0=0xFF: It means the SMULL is not initialized. |
Notice:
If the initialization of SMULL fails, any SMULL related command that is issued will result in receiving the following response containing an error code 0xFF.
Command Code 0x00 0x01 0xFF
Get SMULL configurations: 0xA042 #
The SMULL configurations consist of 7 parameters: mode, slave number, slave ID, PHY rate, SYNC address, maximum length of downlink private packet and maximum length of uplink private packet. You can get all settings by issuing this command.
Send: 0xA0 0x42 0x00 0x00
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x42 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (LSB) |
The length of data in successful response differs from that in failure response.
Successful response: 0xA0 0x42 0x00 0x0C B0~B11
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x42 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x0C | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | Mode 0x00: slave 0x01: master |
| B1 | Slave Number. The maximum number of slaves that is used in your application. |
| B2 | Slave ID. 0~ (slave number – 1). Master will ignore this value. |
| B3 | PHY Rate. 1: 1Mbps, 2: 2Mbps. Other values will be considered as invalid. |
| B4 | SYNC Address (MSB) |
| B5 | SYNC Address |
| B6 | SYNC Address |
| B7 | SYNC Address (LSB) |
| B8 | Maximum Length of Downlink Private Packet (MSB) |
| B9 | Maximum Length of Downlink Private Packet (LSB) |
| B10 | Maximum Length of Uplink Private Packet (MSB) |
| B11 | Maximum Length of Uplink Private Packet (LSB) |
Failure response: 0xA0 0x42 0x00 0x01 0x01
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x42 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x01 | Data Length (LSB) |
| 0x01 | Fail |
Set SMULL configurations: 0xA043 #
As aforementioned, the SMULL configurations include 7 parameters. You can set these parameters all at once by issuing this command.
Send: 0xA0 0x43 0x00 0x0C B0~B11
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x43 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x0C | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | Mode 0x00: slave 0x01: master |
| B1 | Slave Number. The maximum number of slaves that may be used in your application. This number must be less than or equal to the value of CFG_IPMAC_MAX_SLV_NUM. As of the current firmware, CFG_IPMAC_MAX_SLV_NUM is set at 64. |
| B2 | Slave ID. 0~ (slave number – 1). Master will ignore this value. |
| B3 | PHY Rate. 1: 1Mbps, 2: 2Mbps. Other values will be considered as invalid. |
| B4 | SYNC Address (MSB) |
| B5 | SYNC Address |
| B6 | SYNC Address |
| B7 | SYNC Address (LSB) |
| B8 | Maximum Length of Downlink Private Packet (MSB) |
| B9 | Maximum Length of Downlink Private Packet (LSB) |
| B10 | Maximum Length of Uplink Private Packet (MSB) |
| B11 | Maximum Length of Uplink Private Packet (LSB) |
Response: 0xA0 0x43 0x00 0x01 B0
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x43 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x01 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | B0=0x00: Success B0=0x01: A general error B0=0x02: Command length is short B0=0x03: Invalid SMULL mode B0=0x04: Invalid slave number B0=0x05: Invalid slave Id B0=0x06: Invalid PHY Rate B0=0x07: Invalid SYNC address B0=0x08: Invalid downlink packet size B0=0x09: Invalid uplink packet size |
Query Connection Status of Each Slave: 0xA044 #
The user can get the connection status of each slave by issuing this command on the master side.
Send: 0xA0 0x44 0x00 0x00
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x42 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (LSB) |
Response: 0xA0 0x44 0x00 0x10 B0~B15
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x44 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x10 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | The connection status of slave0 ~ slave7 |
| … | … |
| B15 | The connection status of slave120 ~ slave127 |
The byte sequence of data B0~B15 is a bit-map, each bit is associated with a slave. B0 is associated with slave0 to slave7, while B1 is associated with slave8 to slave15, and so on. A value of one for the bit indicates that the corresponding slave is connected to the master. Below, we provide two examples to show what a response might look like.
Example1: Assuming that the maximum number of slaves is set to four and that all four slaves are connected to the master, the response would be 0xA0 0x44 0x00 0x10 0x0F 0x00…0x00. However, in the case where only slaves 0 and 3 are connected, the response would be 0xA0 0x44 0x00 0x10 0x09 0x00…0x00.
Example2: Assuming that the maximum number of slaves is set to nine and that all nine slaves are connected to the master, the response would be 0xA0 0x44 0x00 0x10 0xFF 0x01 0x00…0x00. However, in the case where only slaves 0, 1, 6, 7 and 9 are connected, the response would be 0xA0 0x44 0x00 0x10 0xB3 0x01 0x00..0x00.
If this command is executed on the slave side, the response would be 0xA0 0x44 0x00 0x01 0x01.
Transmit Data: 0xA048 #
This command is used for data transmission between the master and slave once the network is successfully established. The master can transmit three types of packet. However, the slave can only trasmit private packets. Below, we will provide a detailed explanation on how to use this command for both the master and the slave.
①Slave transmits data. The slave can only transmit private packets, so the command sequence is relatively simple.
Send: 0xA0 0x48 D0 D1 B0~Bn
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x48 | Command Code (LSB) |
| D0 | Data Length (MSB) |
| D1 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | first byte of data |
| … | … |
| Bn | last byte of data |
Response: 0xA0 0x48 0x00 0x01 B0
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x44 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x01 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | B0=0x00: Success B0=0x01: Fail B0=0x02: The length of transmitted data is too long |
②Master transmits data. The master can transmit three types of packets to the slave: private, public and broadcast. In current firmware, we only support private packet.
Send: 0xA0 0x48 D0 D1 T0 S0 B0~Bn
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x48 | Command Code (LSB) |
| D0 | Data Length (MSB) |
| D1 | Data Length (LSB) |
| T0 | Packet type 0x00: broadcast 0x01: public 0x02: private |
| S0 | Slave ID. If sending a private packet, it is necessary to specify which slave it is sent to. |
| B0 | first byte of data |
| … | … |
| Bn | last byte of data |
Response: 0xA0 0x48 0x00 0x01 B0
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x48 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x01 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | B0=0x00: Success B0=0x01: Fail B0=0x02: The length of transmitted data is too long B0=0x03: Invalid slave ID |
Receive Data: 0xA049 #
When the master receives data from the slave(s) or vice versa, the received data will be transmitted to the user in the following format.
0xA0 0x49 D0 D1 S0 B0~Bn
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x49 | Command Code (LSB) |
| D0 | Data Length (MSB) |
| D1 | Data Length (LSB) |
| S0 | If data is received by the master, S0 denotes the slave ID. If data is received by the slave, S0 denotes the packet type (0 = broadcast, 1 = public, 2 = private). |
| B0 | first byte of data |
| … | … |
| Bn | last byte of data |
Get UART Configuration: 0xA063 #
This command read the UART configuration.
Send: 0xA0 0x63 0x00 0x00
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x63 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (LSB) |
Successful Response: 0xA0 0x63 0x00 0x08 B0~B7
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x63 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x08 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | Baud rate (MSB) |
| B1 | Baud rate |
| B2 | Baud rate |
| B3 | Baud rate (LSB) |
| B4 | Data Bits |
| B5 | Stop Bits |
| B6 | Parity, 0-no parity, 1-odd parity, 2-even parity |
| B7 | Flow Control |
Response with errors: 0xA0 0x63 0x00 0x01 0x01
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x63 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x01 | Data Length (LSB) |
| 0x01 | Fail |
Configure UART: 0xA064 #
This command writes the UART configuration.
Send: 0xA0 0x64 0x00 0x08 B0~B7
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x64 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x08 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | Baud rate (MSB) |
| B1 | Baud rate |
| B2 | Baud rate |
| B3 | Baud rate (LSB) |
| B4 | Data Bits |
| B5 | Stop Bits |
| B6 | Parity, 0-no parity, 1-odd parity, 2-even parity |
| B7 | Flow Control |
The maximum supported baud rate is 2000000.
Response: 0xA0 0x64 0x00 0x01 B0
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x64 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x01 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | B0=0x00: Success B0=0x01: Fail |
Get UART Baudrate: 0xA065 #
Send: 0xA0 0x65 0x00 0x00
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x65 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (LSB) |
Response: 0xA0 0x65 0x00 0x04 B0~B3
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x65 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x04 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | Baud rate (MSB) |
| B1 | Baud rate |
| B2 | Baud rate |
| B3 | Baud rate (LSB) |
Set UART Baudrate: 0xA066 #
Send: 0xA0 0x66 0x00 0x04 B0~B3
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x66 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | Baud rate (MSB) |
| B1 | Baud rate |
| B2 | Baud rate |
| B3 | Baud rate (LSB) |
Response: 0xA0 0x66 0x00 0x01 B0
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0x66 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x01 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | B0=0x00: Success B0=0x01: Fail |
Chip Reset: 0xA0E1 #
Typically, when the SMULL parameters are updated, it is recommended to reset the chip by issuing this command.
Send: 0xA0 0xE1 0x00 0x00
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0xE1 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (LSB) |
Response: 0xA0 0xE1 0x00 0x01 B0
| Byte | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Command Code (MSB) |
| 0xE1 | Command Code (LSB) |
| 0x00 | Data Length (MSB) |
| 0x01 | Data Length (LSB) |
| B0 | B0=0x00: Success B0=0x01: Fail |
Example #
Before initiating data transmission, it is crucial to set up a network connection - a process also referred to as pairing. To guarantee effective network communication, it is imperative that the SMULL configurations of both the master and each slave must be identical, with the exception of the mode and slave ID. Employing UART for SMULL configuration paves the way for this essential uniformity between the master and all slave devices. To elucidate this setup procedure, we will walk through an illustrative example. The specifications for each network parameter are detailed hereinbelow.
- Mode: (master: 0x01, slave: 0x00)
- Slave number: 4
- Slave Id: (0x00 ~ 0x03), master will ignore this value
- Phyrate: 2M
- Address: 0x2954935B
- Maximum length of downlink packet: 10bytes
- Maximum length of uplink packet: 100bytes
Two methods can be used to complete the configuration. Method 1 requires the use of command 0xA043, whereas method 2 entails a combination of commands 0xA01A, 0xA012, 0xA014, 0xA018, 0xA016, 0xA01C, 0xA01E. Once the configuration is completed successfully, it is necessary to execute the reset command.
Method1:
The command sequence issued by the master would be
①0xA0 0x43 0x00 0x0C 0x01 0x04 0x00 0x02 0x29 0x54 0x93 0x5B 0x00 0x0A 0x00 0x64
②0xA0 0xE1 0x00 0x00
The command sequence issued by each slave (slave0~slave3) would be
①0xA0 0x43 0x00 0x0C 0x00 0x04 ID 0x02 0x29 0x54 0x93 0x5B 0x00 0x0A 0x00 0x64
②0xA0 0xE1 0x00 0x00
Method2:
The command sequence issued by the master would be
①0xA0 0x1A 0x00 0x01 0x01
②0xA0 0x12 0x00 0x01 0x04
③0xA0 0x14 0x00 0x01 0x00
④0xA0 0x18 0x00 0x01 0x02
⑤0xA0 0x16 0x00 0x04 0x29 0x54 0x93 0x5B
⑥0xA0 0x1C 0x00 0x02 0x00 0x0A
⑦0xA0 0x1E 0x00 0x02 0x00 0x64
⑧0xA0 0xE1 0x00 0x00
The command sequence issued by each slave would be
①0xA0 0x1A 0x00 0x01 0x00
②0xA0 0x12 0x00 0x01 0x04
③0xA0 0x14 0x00 0x01 ID (different slave ID)
④0xA0 0x18 0x00 0x01 0x02
⑤0xA0 0x16 0x00 0x04 0x29 0x54 0x93 0x5B
⑥0xA0 0x1C 0x00 0x02 0x00 0x0A
⑦0xA0 0x1E 0x00 0x02 0x00 0x64
⑧0xA0 0xE1 0x00 0x00
In method2, the order of the command sequence is not mandatory. However, the command 0xA014 should be issued after 0xA012 and the reset command must be the final one.